Understanding the Importance of
Carbon Sequestration
Carbon Sequestration
The White House and USDA are reportedly developing plans to use $30 billion in funds from the Commodity Credit Corporation (CCC) for the creation of a carbon bank program, which would involve giving carbon credits to farmers and landowners in return for adopting carbon sequestration practices, which they could then sell in a cap and trade market
-
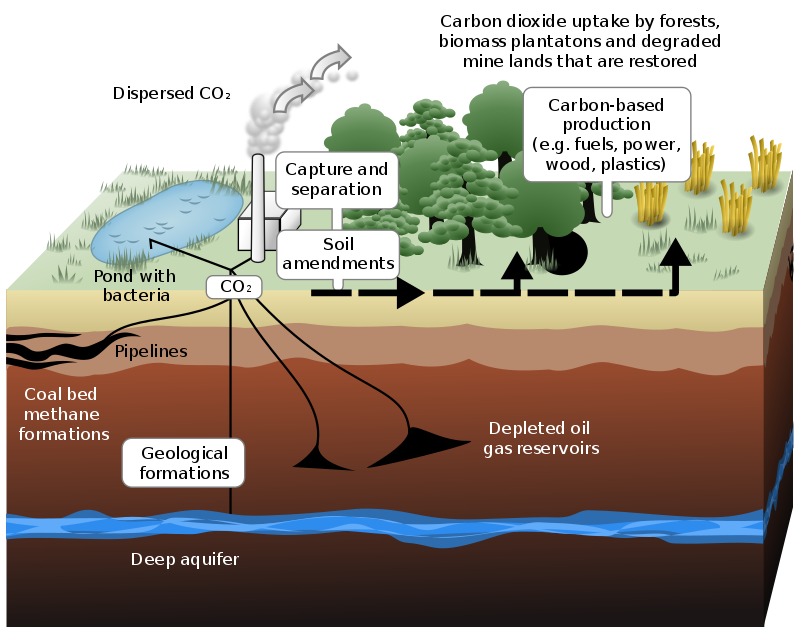
Carbon sequestration is the process of storing carbon in a carbon pool. Carbon dioxide (CO2) is naturally captured from the atmosphere through biological, chemical, and physical processes. These changes can be accelerated through changes in land use and agricultural practices, such as converting cropland into land for non-crop fast-growing plants. Artificial processes have been devised to produce similar effects, including large-scale, artificial capture and sequestration of industrially produced CO2 using subsurface saline aquifers, reservoirs, ocean water, aging oil fields, or other carbon sinks, bio-energy with carbon capture and storage, biochar, ocean fertilization, enhanced weathering, and direct air capture when combined with storage.
-
The likely need for CDR (carbon dioxide removal) has been publicly expressed by a range of individuals and organizations involved with climate change issues, including IPCC chief Rajendra Pachauri, the UNFCCC executive secretary Christiana Figueres, and the World Watch Institute. Institutions with major programs focusing on CDR include the Lenfest Center for Sustainable Energy at the Earth Institute, Columbia University, and the Climate Decision Making Center, an international collaboration operated out of Carnegie-Mellon University's Department of Engineering and Public Policy.
-
The purpose of the CCX is to purchase carbon sequestration credits from landowners who have implemented carbon sequestering practices on their lands and sell those credits to carbon-emitting companies and industries, thereby reducing their net carbon emissions.
Growing Climate Solutions Act
News Articles of Carbon Sequestration
-
Microsoft Metrics: Carbon Removal Portfolio FY21
Microsoft is doing its part. They are an example of corporate leadership in ecological stewardship.
-
Microsoft carbon removal. Lessons from an early corporate purchase.
Achieving our carbon-negative goal by 2030 will require more than carbon reduction—Microsoft must also physically remove carbon from the atmosphere. Today, carbon removal is far from mainstream, however, and the market for corporate procurement of carbon removal is relatively undeveloped.
-
National Geographic Carbon Sequestration Article
National Geographic articleGreen Diamond Resource Company, Microsofts top contractor by volume, is participating in Carbon Sequestration